Forex Trading Basics and Key Terms For Beginners 2024
Gaining a thorough understanding of the complex jargon and foundations of forex trading is crucial to successfully navigate the world’s currency markets. This thorough book breaks down the essential components, offering understanding of the basis of forex trading and introducing terms that all traders should be familiar with.
1. Fundamentals of the Forex Market: –
The decentralized worldwide marketplace where currencies are traded is known as the foreign exchange (forex) market.
– Participants: Banks, financial institutions, businesses, governments, and individual traders are some of the major players.
– 24-Hour Trading: Forex is open for business five days a week, 24 hours a day, and facilitates continuous trading across time zones.
2. Pairs of currencies:
– Major Pairs: These include the most traded currencies in the world, including USD/JPY, GBP/USD, and EUR/USD.
– Minor (Cross) Pairs: These pairs, such as EUR/GBP or AUD/JPY, do not use the US dollar.
– Exotic Pairs: Put two big currencies together, such as USD/TRY or EUR/SGD, with a currency from a developing economy.
3. Prices to Bid and Ask:
– Bid Price: The amount a trader is willing to pay to sell a pair of currencies.
– Ask Price: The cost a trader will pay to purchase a pair of currencies.
Spread: The amount that represents transaction expenses and is the difference between the ask and bid prices.
4. Margin and Leverage:
Leverage is a strategy that lets traders manage a sizable position with a comparatively small sum of money.
Margin: The sum of money needed to start and keep a leveraged trade.
5. Pip and Lot Sizes: –
Pip: Usually the fourth decimal point, the lowest price adjustment that a specific exchange rate may make.
– Lot Sizes: The differences in transaction sizes represented by Standard, Mini, and Micro lots impact both possible profit and risk.
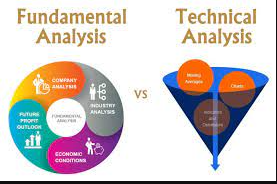
6. Fundamental Analysis: –
Economic Indicators: GDP growth, employment rates, inflation, and interest rates are important variables.
– Central Banks: The Federal Reserve and other central banks have a big influence on currency values through their decisions.
– Political Stability: A nation’s political climate and stability have an impact on the strength of its currency.
7. Examining Technical Data:
– Candlestick Patterns: Doji, engulfing, and hammer patterns are used to analyze market fluctuations.
Support and Resistance: These are the levels that prices have, on average, found it difficult to go above (resistance) or below (support).
8. Risk management:
Stop-Loss Orders: Traders can minimize losses by exiting losing trades at certain points.
Take-Profit Orders: These orders set target levels so that trades are automatically closed at a profit.
Set off on an adventure into the realm of foreign exchange trading, where mastery of the principles and essential jargon is your ticket to prosperity. This book delves deeply into the fundamentals of the forex market, giving you the information you need to make wise choices and maybe increase your trading profits.
Learn about the fundamentals, including bid and ask prices and the behavior of currency pairs, and gain an understanding of the impactful ideas of margin and leverage. Discover the importance of pip and lot sizes as key indicators of risk and potential reward. Explore the worlds of technical and fundamental analysis, where trading tactics are shaped by chart patterns, central bank policies, and economic indicators.
Learn how to minimize risk by protecting your investments with take-profit and stop-loss orders. Learn the value of trading around the clock to take advantage of chances in a market that is constantly changing and dynamic.
Equipped with this thorough understanding of the terminology and principles of forex trading, you’re ready to handle the intricacies of the world’s currency markets. Knowing these essential components will help you become a better trader and make your forex trading experience more profitable, regardless of your level of experience.